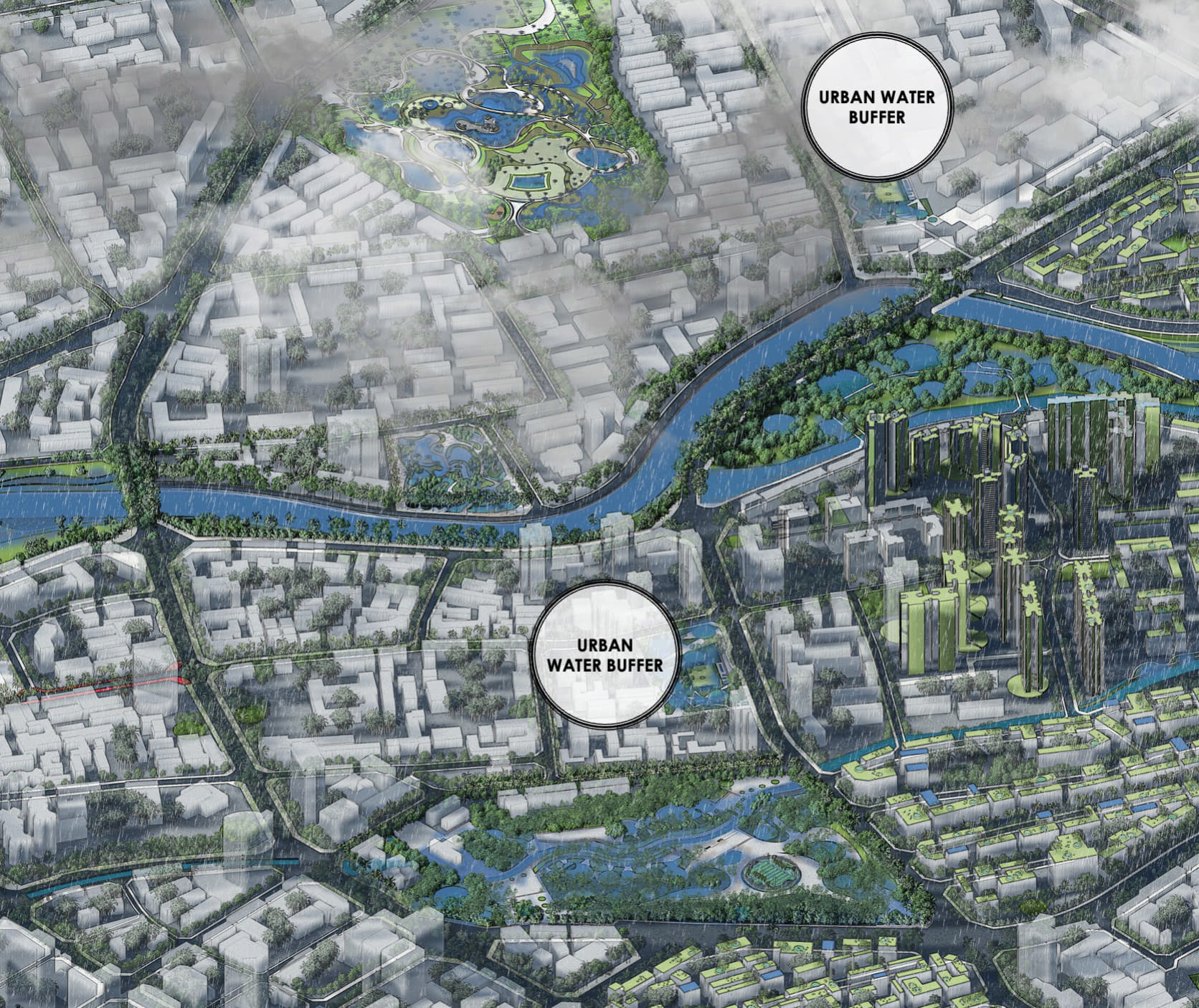
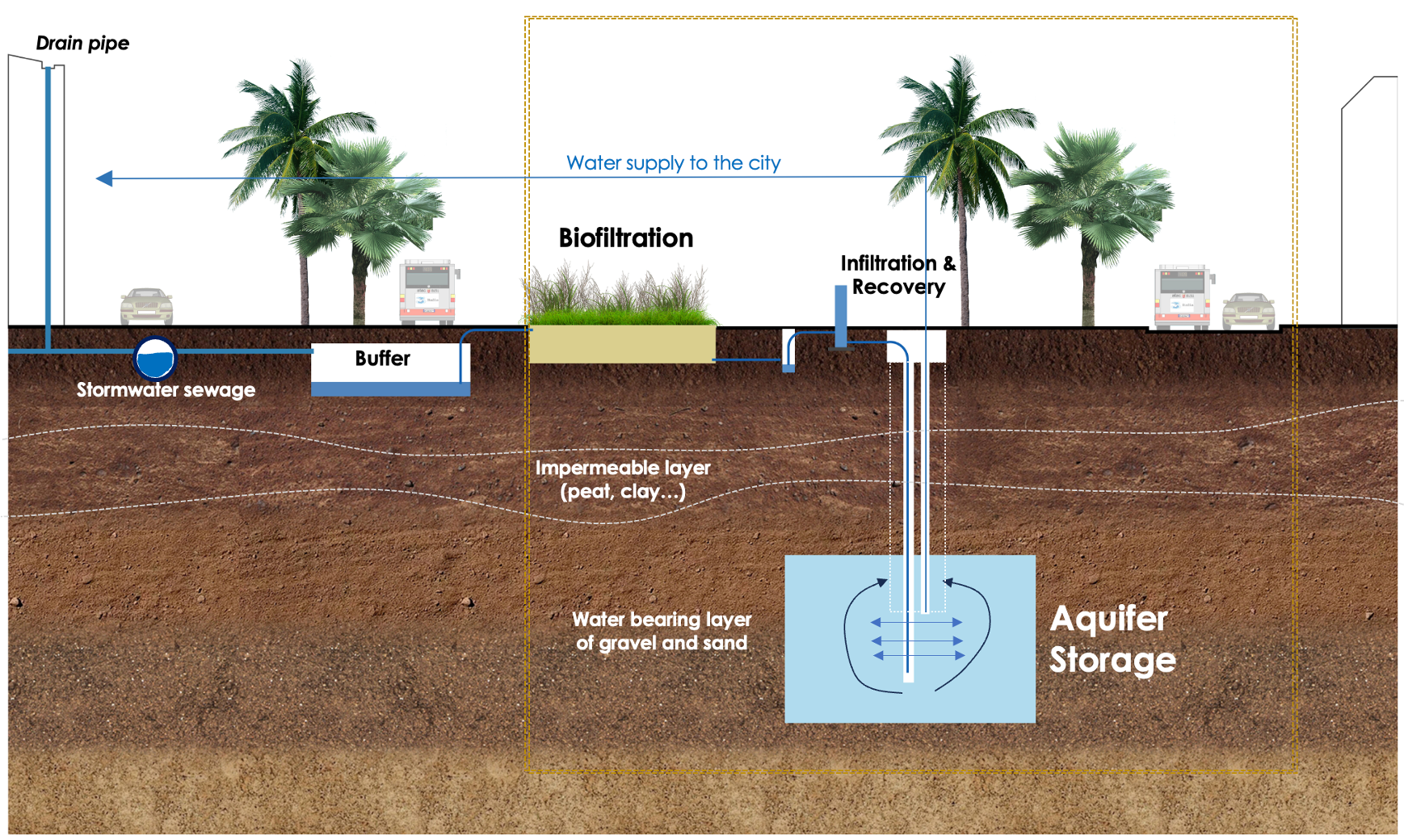
The urban water buffers is a NbS designed to enhance resilience to floods, aquifer depletion, land subsidence, and other climate-related risks. These systems collect, store, and infiltrate excess stormwater into aquifers during heavy rainfall, mitigating urban flooding, replenishing groundwater supplies, and preventing land subsidence caused by excessive groundwater extraction.
In industrial zones and along transport infrastructure, water buffers can reduce runoff, improve water quality through natural filtration, and serve as reservoirs for non-potable water use. Drawing inspiration from the Netherlands, urban water buffer systems in Southeast Asia can implement similar multifunctional solutions that integrate technical features (retention ponds, underground reservoirs, and bioretention cells) with landscape attributes like green corridors, public parks, and biodiversity habitats.
Economically, these buffers lower infrastructure repair costs from flood damage and support urban water security, while socially, they enhance urban aesthetics, provide recreational spaces, and foster community engagement in water stewardship.
The application of urban water buffers in cities like Jakarta, Bangkok, and Ho Chi Minh City could significantly improve climate resilience while addressing urban water challenges in diverse settings.