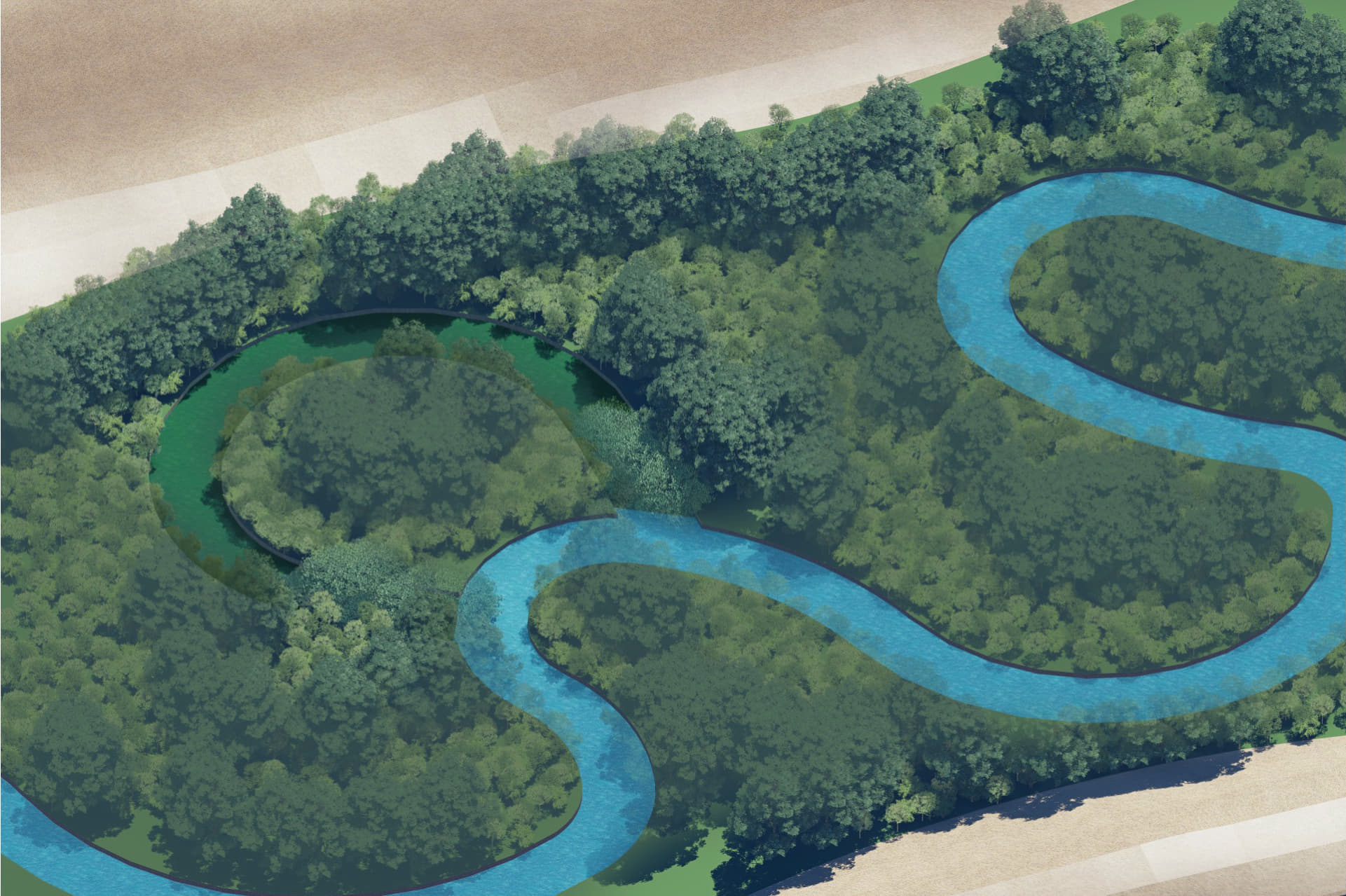
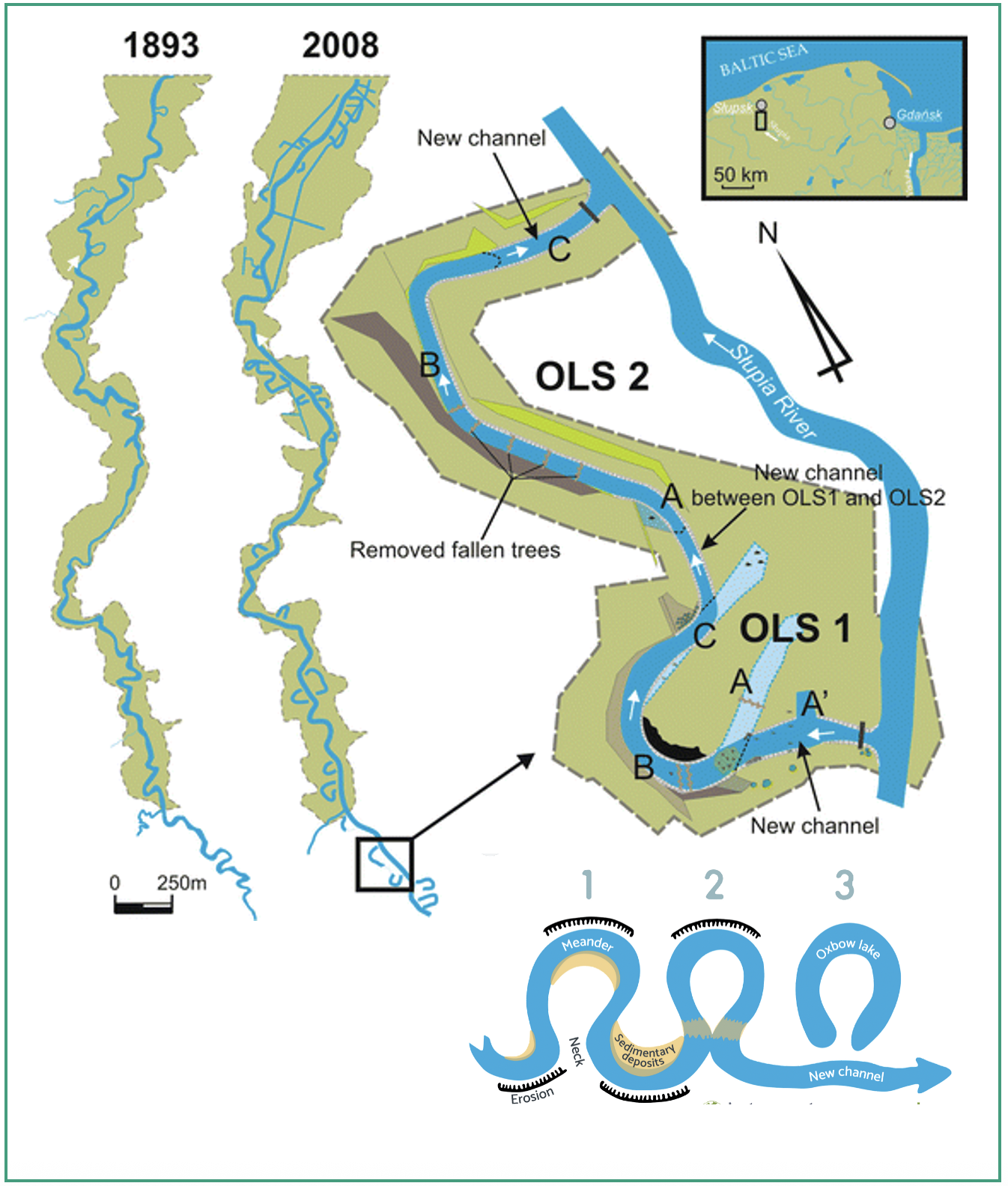
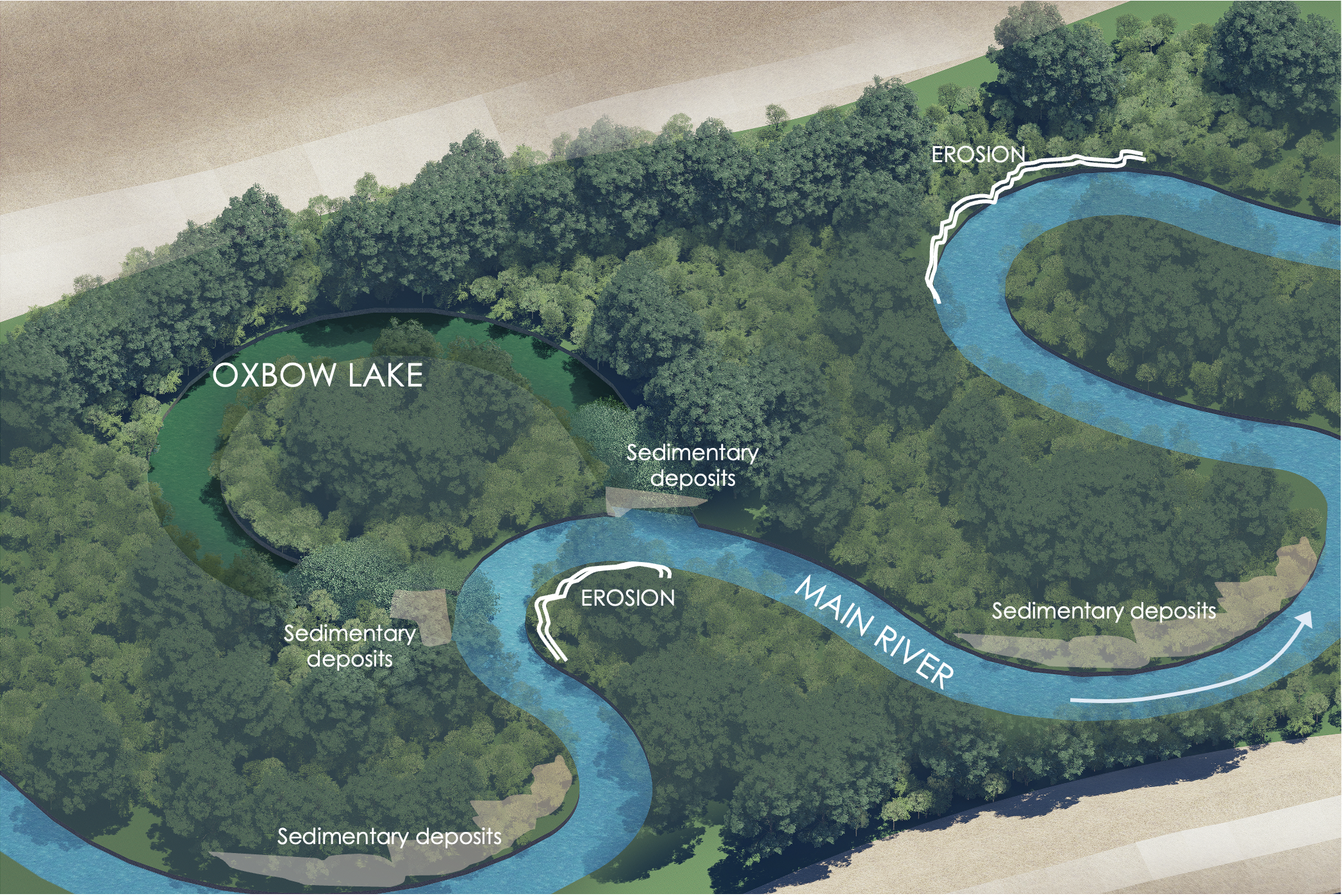
Reconnecting an oxbow lake and its river involves re-establishing the natural hydrological connection between an oxbow lake (a crescent-shaped lake formed by a meander of a river) and the main river channel.
Over time, oxbow lakes can become isolated from the river due to natural processes like sediment deposition or human intervention, such as levee construction or channelization.
Reconnection efforts aim to restore the flow of water between the river and the oxbow, enhancing the health of both water bodies.
This process often involves breaching or removing physical barriers, such as levees or embankments, that have cut off the oxbow from the river. By restoring this connection, water can flow freely between the river and the oxbow, allowing for seasonal flooding, nutrient exchange, and sediment deposition.
These actions help improve water quality, increase biodiversity, and create new habitats for fish, amphibians, and other aquatic species.