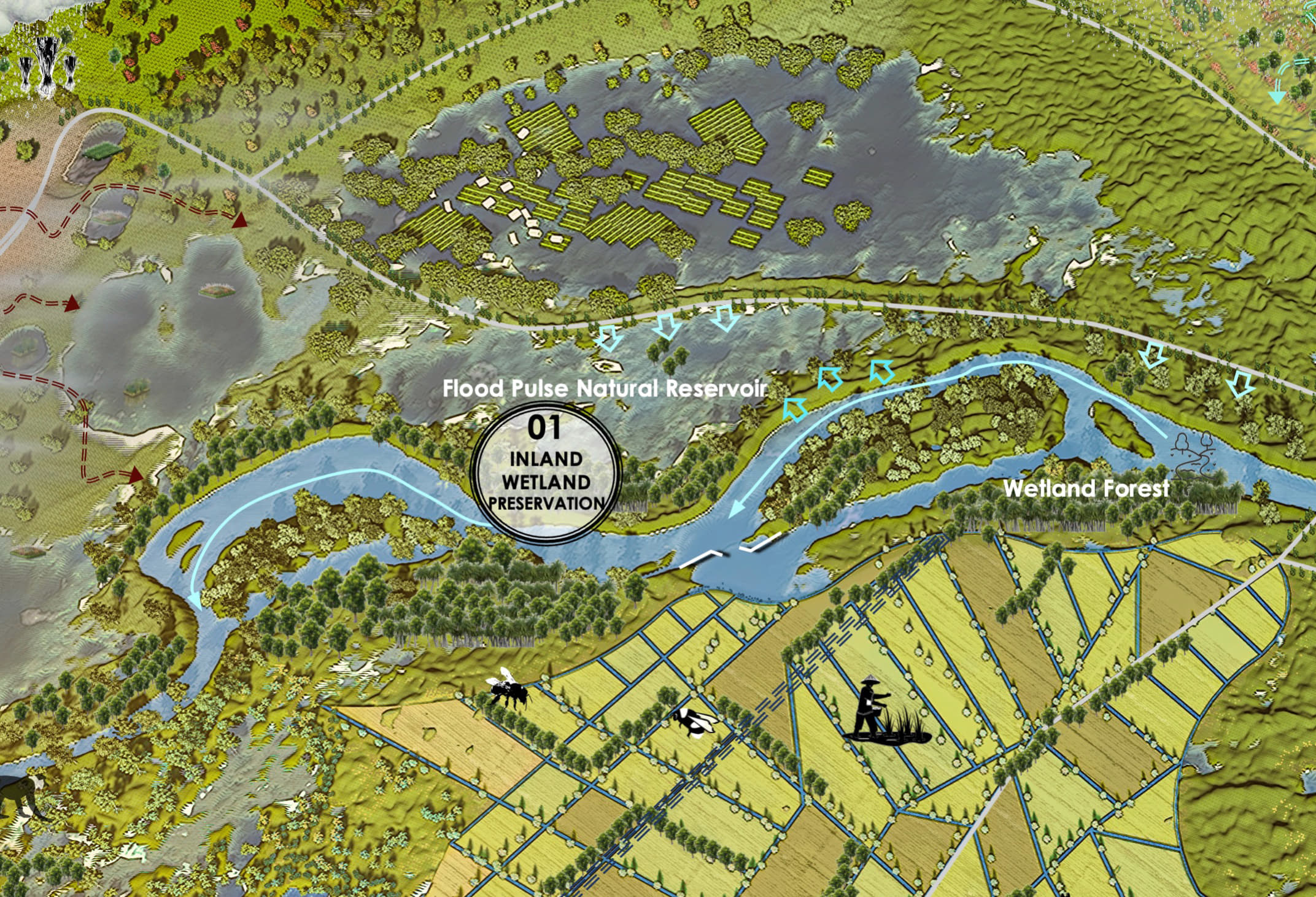
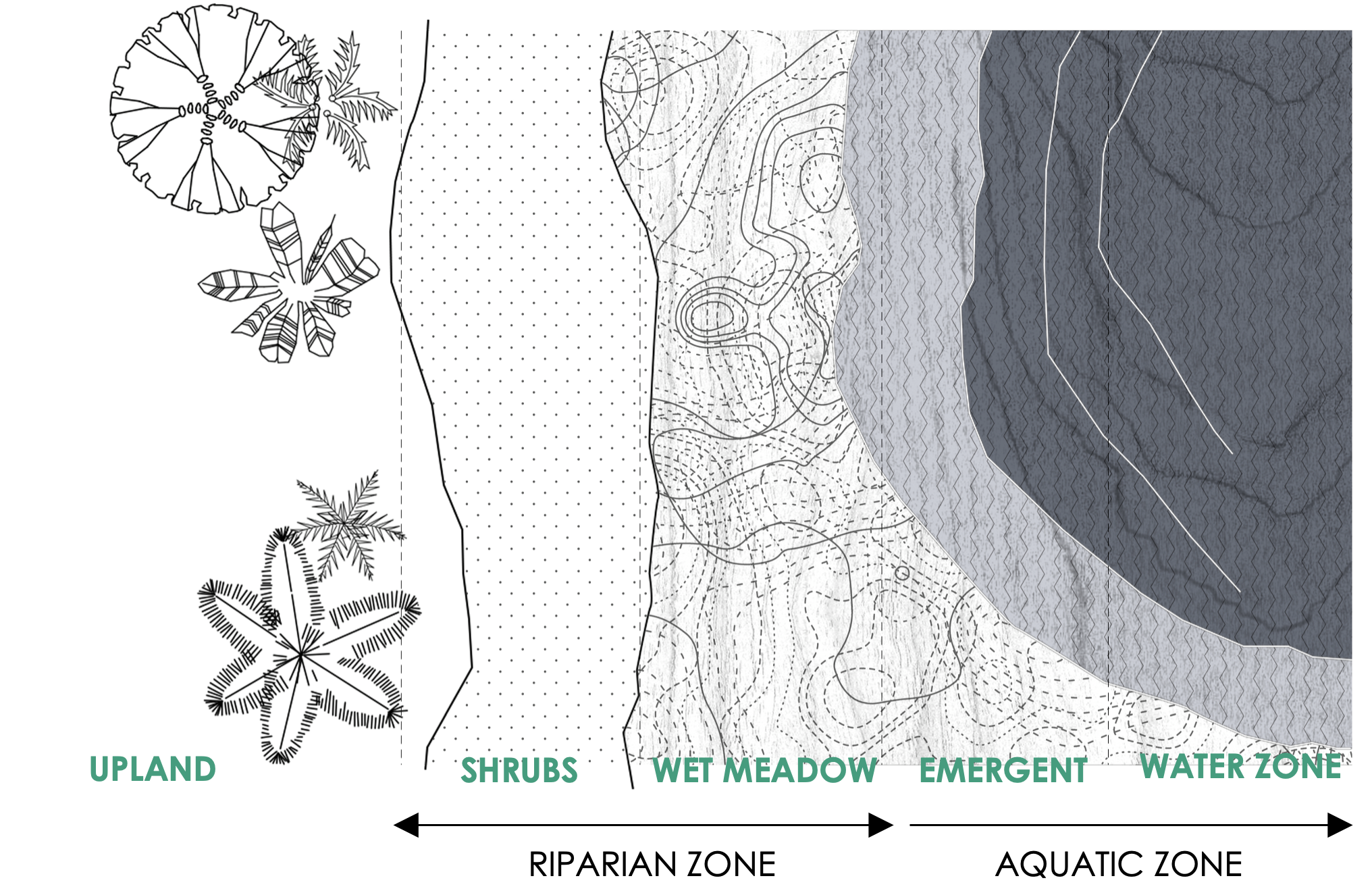
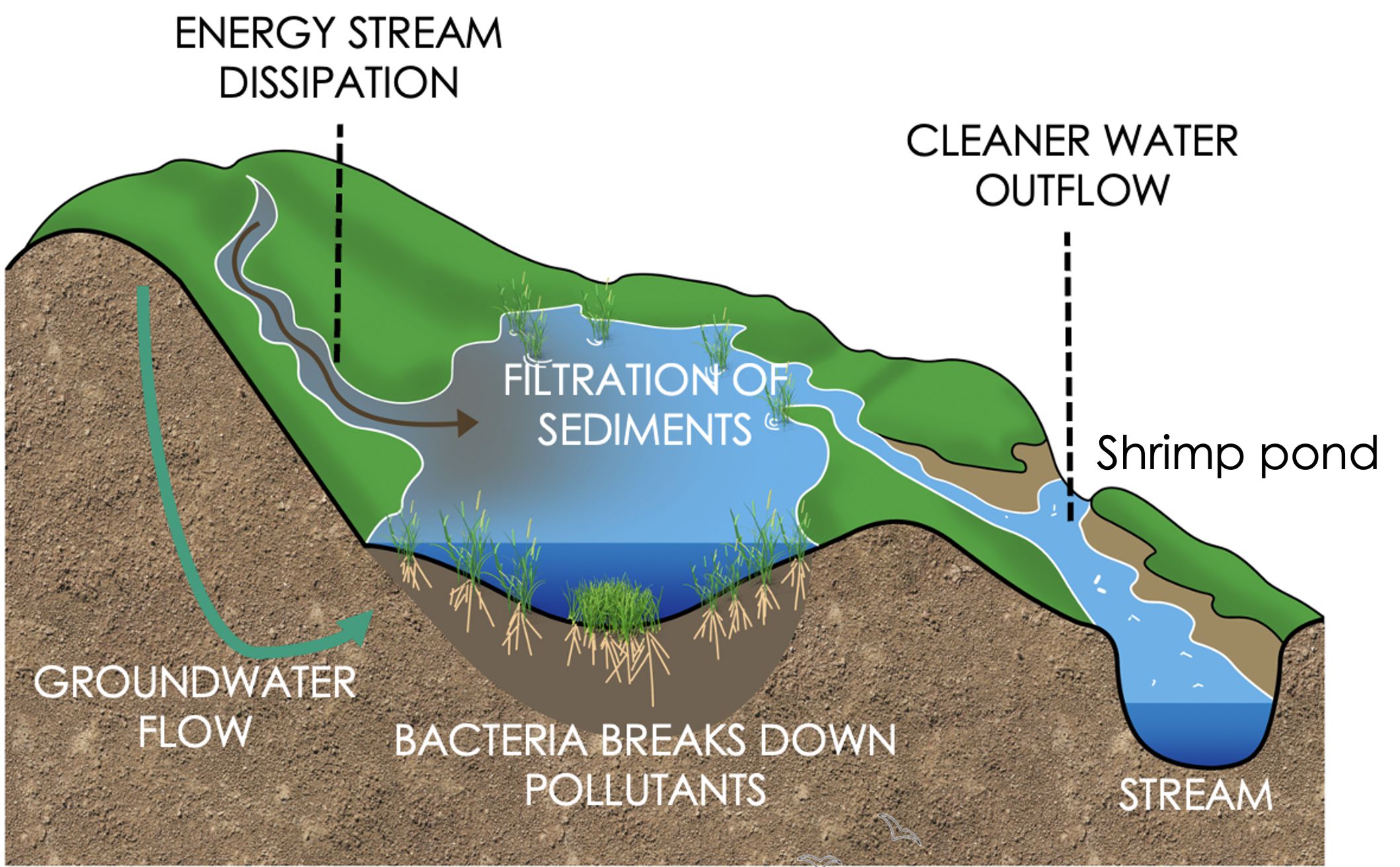
Riparian wetland restoration and preservation focuses on rejuvenating critical freshwater ecosystems by reinstating their natural hydrology and vegetation. Restoration efforts often involve reconnecting floodplains to their rivers by breaching levees, removing barriers, or regrading streambanks to allow seasonal flooding. This hydrological reconnection fosters sediment deposition and nutrient exchange, rebuilding the wetland platform and creating conditions for plant growth.
Techniques such as using biodegradable materials, like coir mats or straw bales, help stabilize banks and retain sediments, while channels, pools, and meanders are reintroduced to restore the natural features of the wetland. These modifications enhance water circulation and provide diverse habitats for fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates.
Native flood-tolerant vegetation, is planted to anchor soils, filter water, and provide shade and habitat.