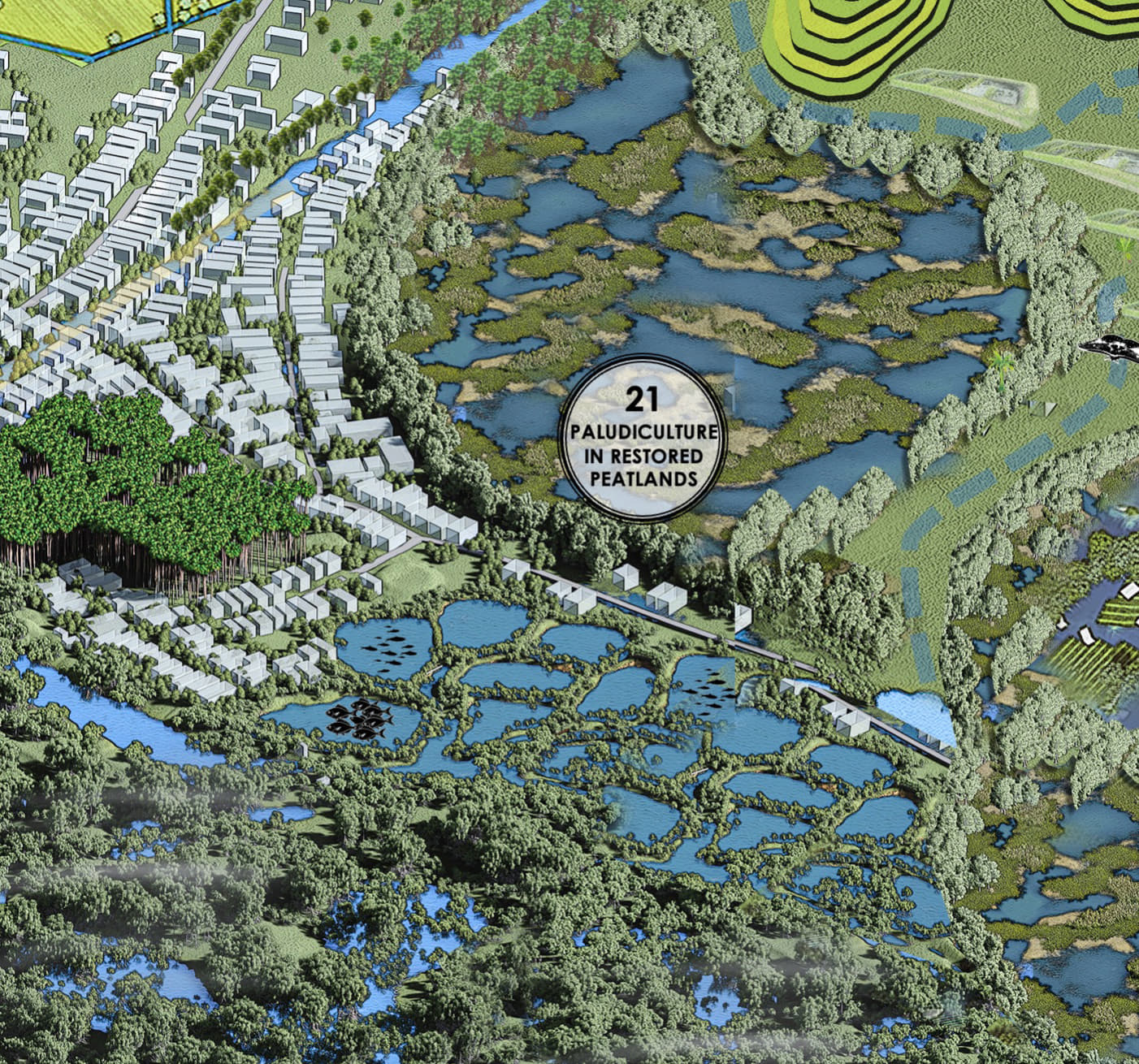
Paludiculture associated peatland is an innovative ecological approach focused on restoring and enhancing peatland ecosystems while supporting biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and ecosystem resilience.
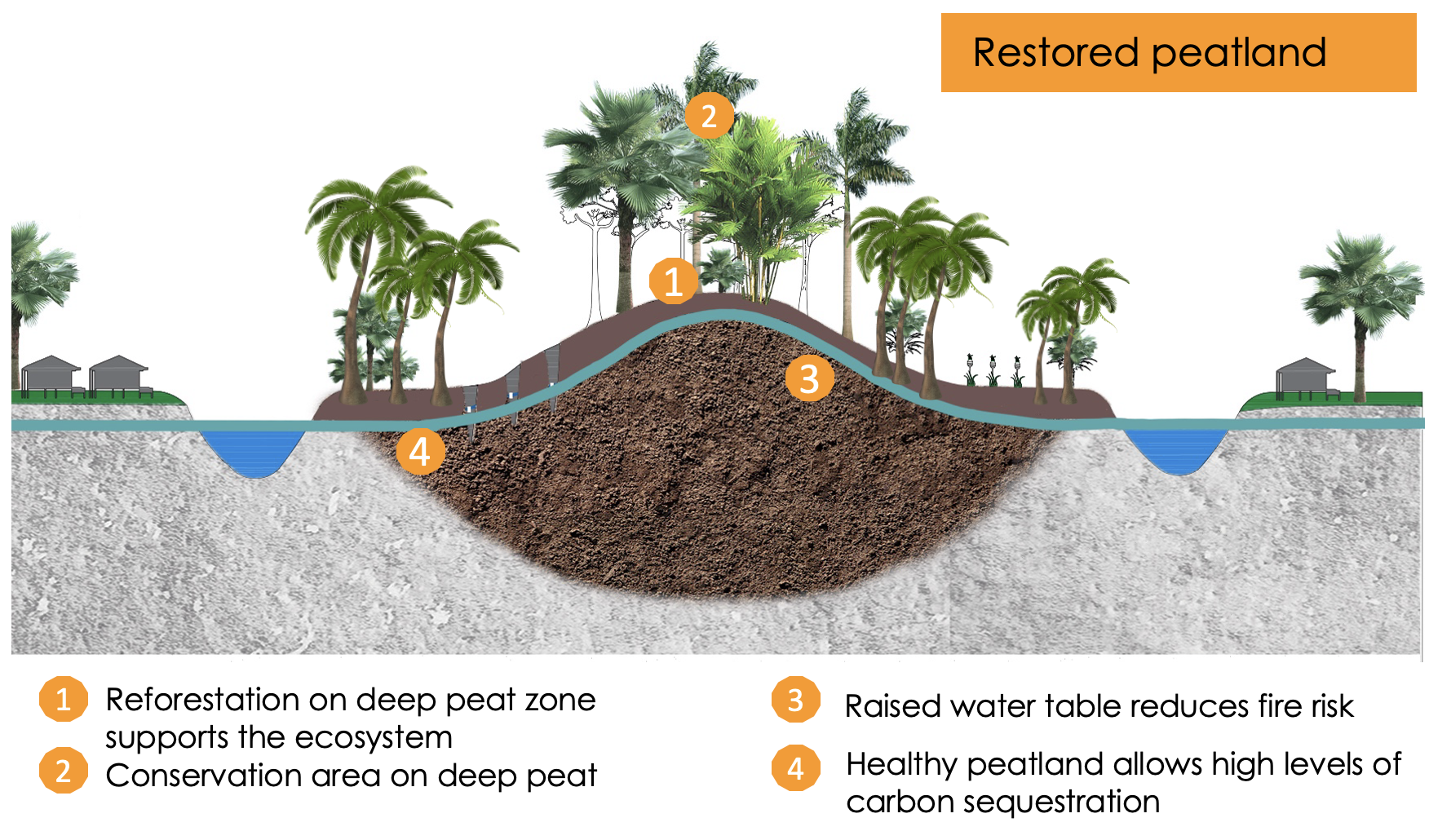
By cultivating water-loving vegetation such as sphagnum moss, reeds, mangroves, aquatic grasses, and marsh plants in waterlogged peatland areas, paludiculture helps stabilize soils, reduce erosion, and restore the natural hydrology of these vital ecosystems.
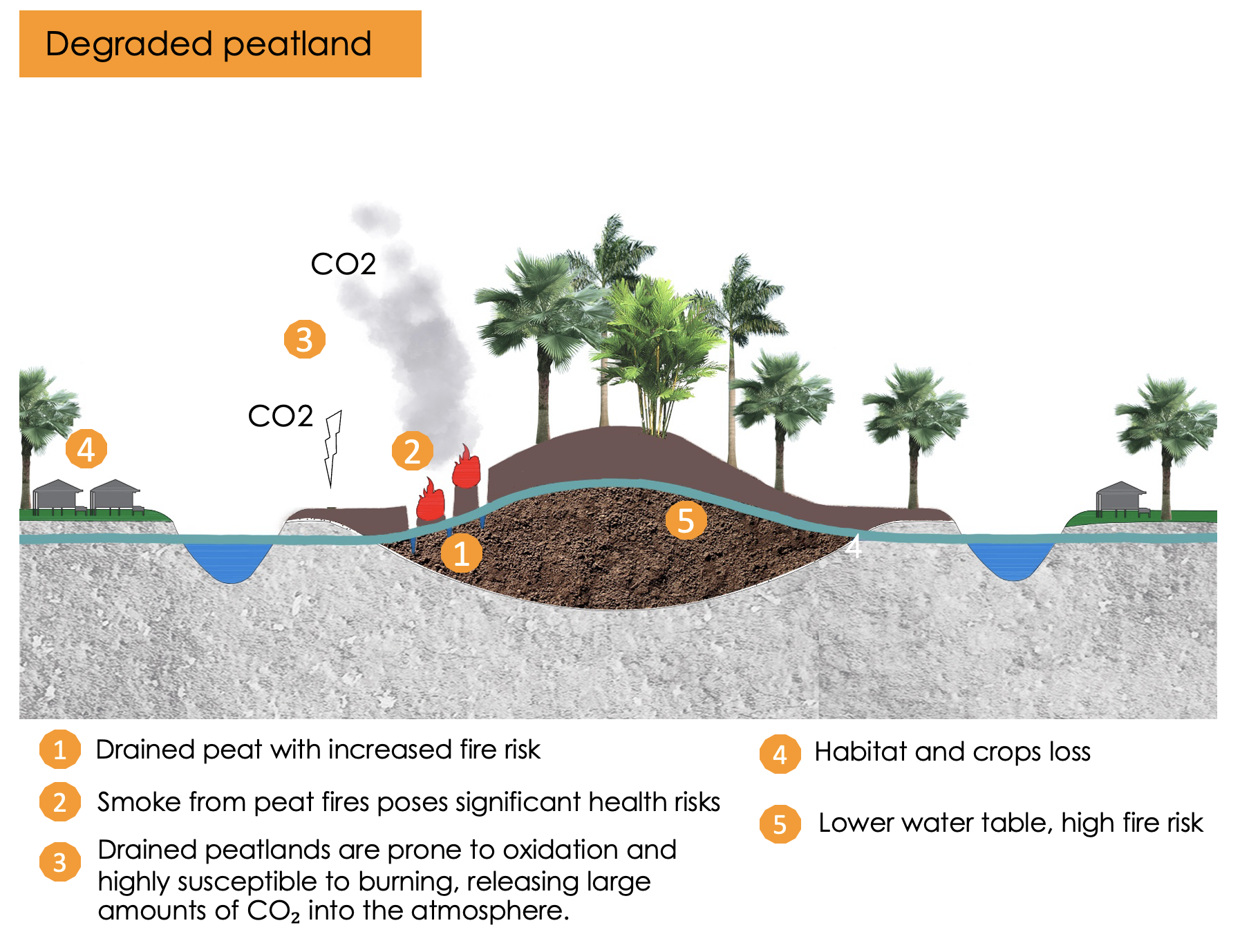
These plants play a crucial role in carbon capture, preventing the release of greenhouse gases from drained peatlands, while providing habitats for diverse wildlife.
In tropical Southeast Asia, paludiculture can contribute to the restoration of degraded peatlands, improve water quality, and promote sustainable land use practices. This approach not only supports biodiversity but also offers economic opportunities by providing sustainable resources for local communities.