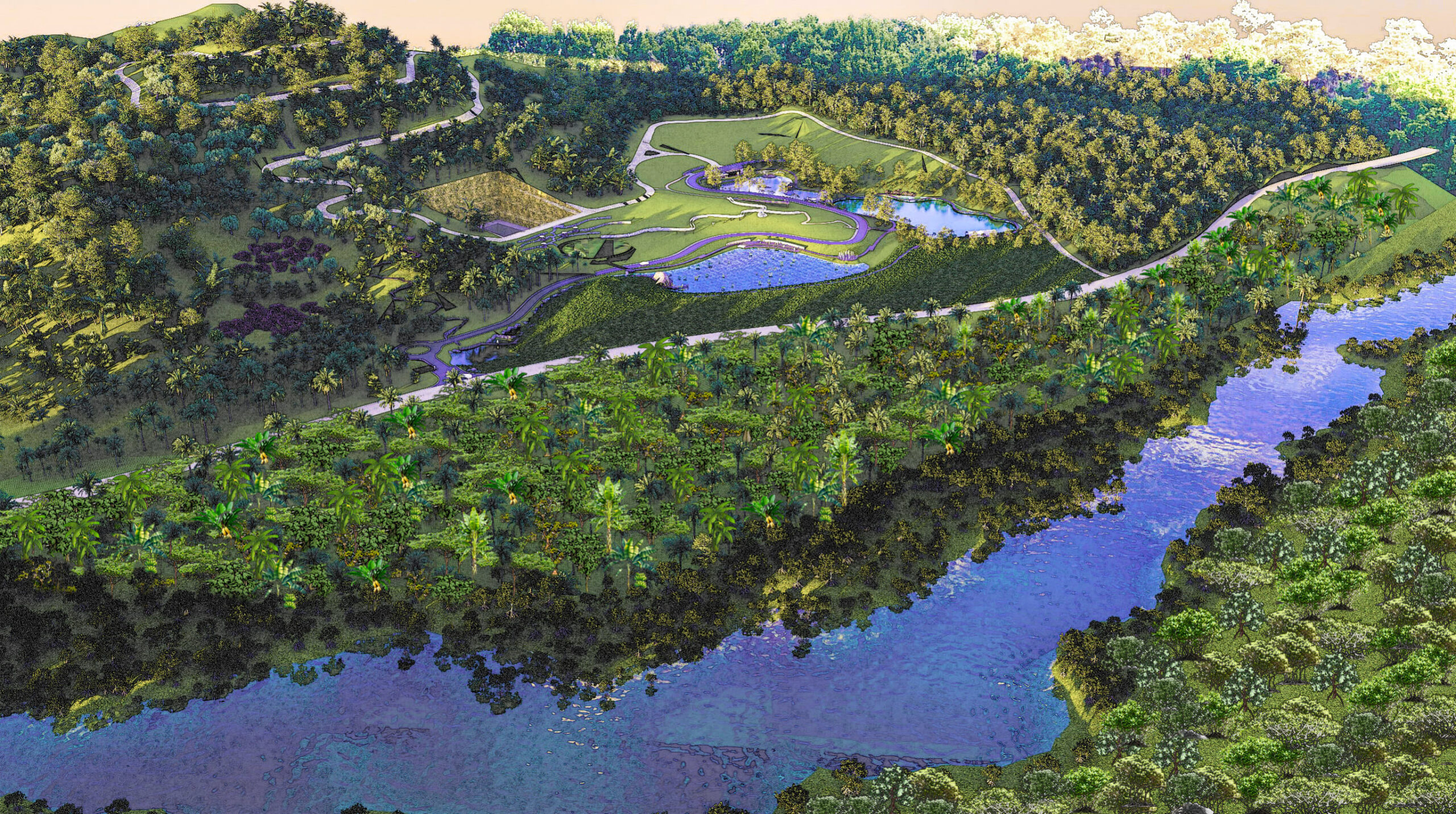
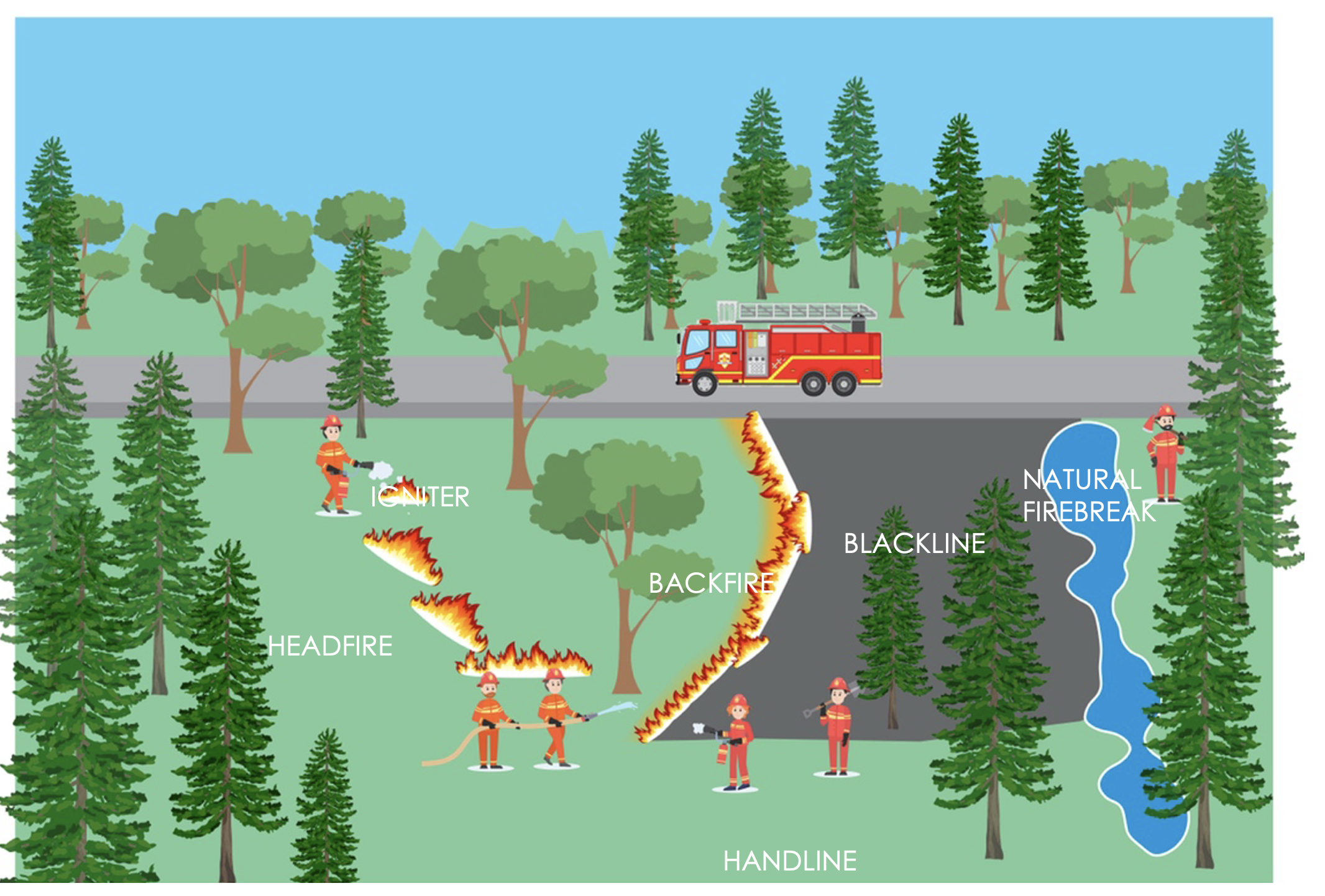
Preventive forest fire and post-fire management as a Nature-based Solution (NbS) aims to integrate technical, landscape, and community-driven approaches to reduce fire risks, restore ecosystems, and enhance resilience to climate change. Techniques include the establishment of firebreaks using native vegetation, controlled burning to reduce fuel loads, and the use of soil moisture-enhancing measures, such as rewetting degraded peatlands to prevent ignition.
Socially, engaging local communities through participatory fire monitoring, traditional fire knowledge, and alternative livelihood programs reduces slash-and-burn practices. Contextually, such strategies are vital for fire-prone regions like Indonesia’s peatlands and Myanmar’s dry forests, where forest fires exacerbate biodiversity loss and greenhouse gas emissions.
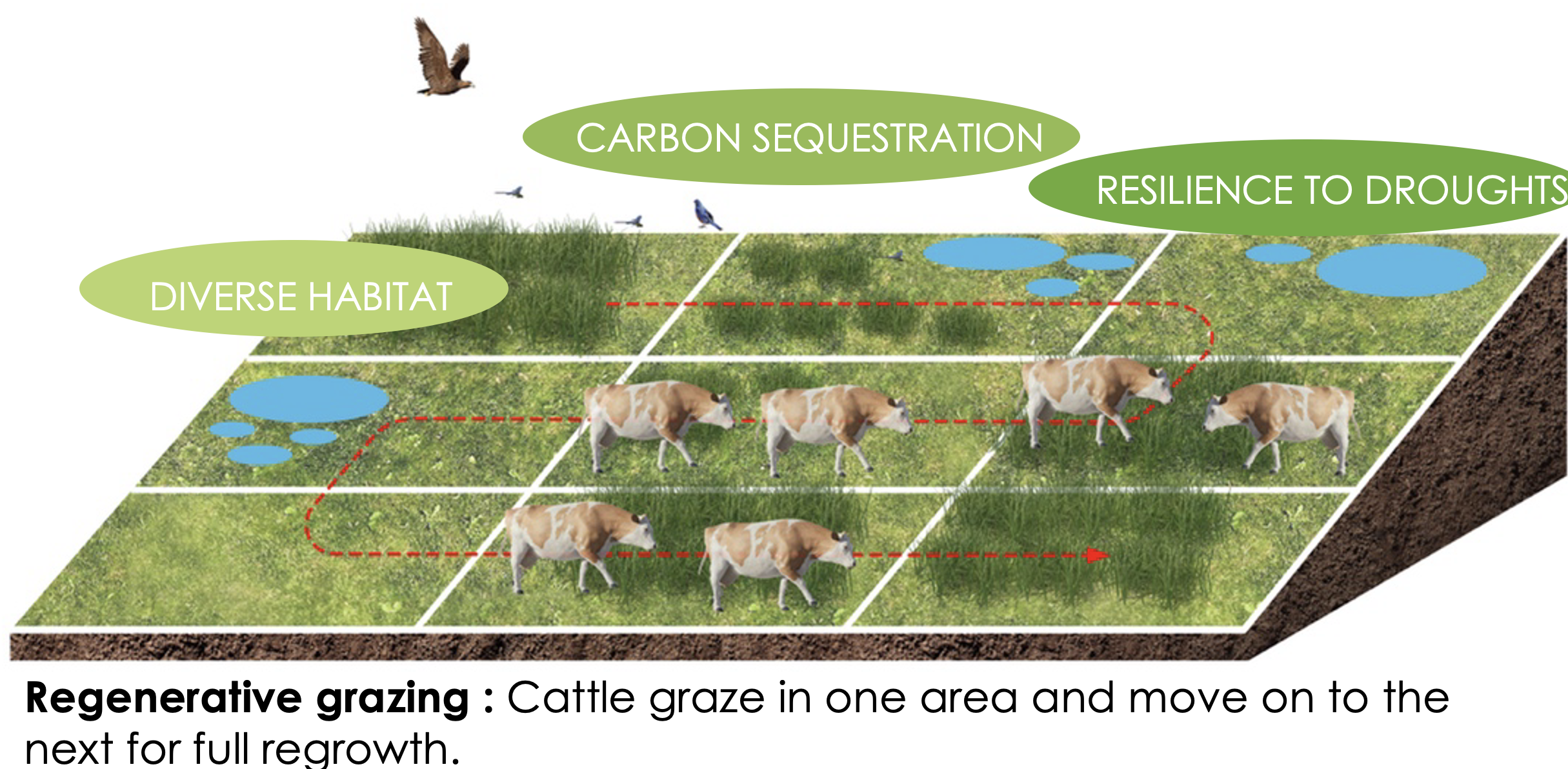
Economically, preventive fire management reduces disaster response costs and enhances ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, water regulation, and agroforestry productivity, while post-fire actions focus on soil stabilization, reforestation with fire-resistant species, and biodiversity recovery.
By addressing both mitigation and adaptation, forest fire management as an NbS contributes to sustainable landscapes, improved livelihoods, and long-term climate resilience in the region.