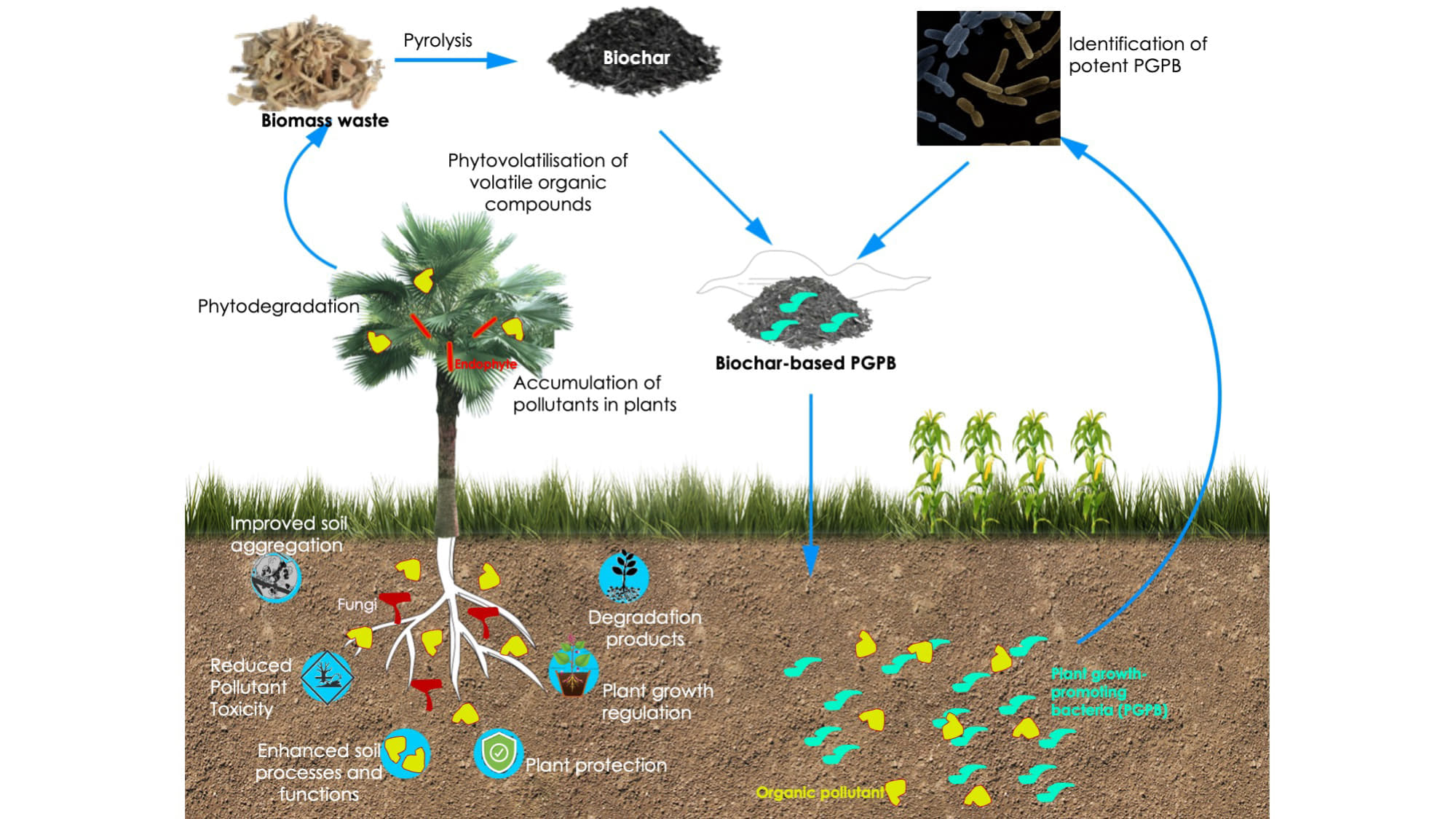
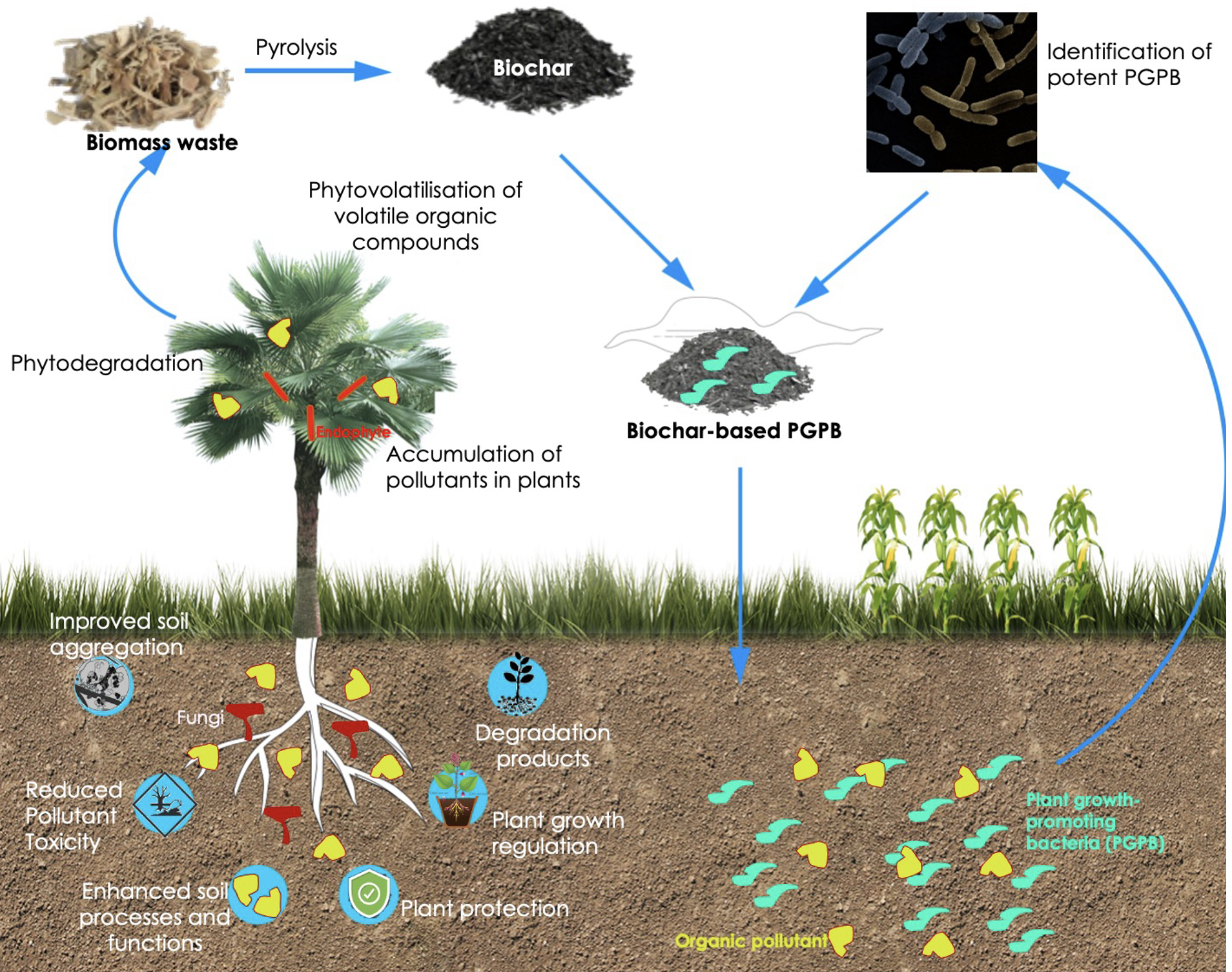
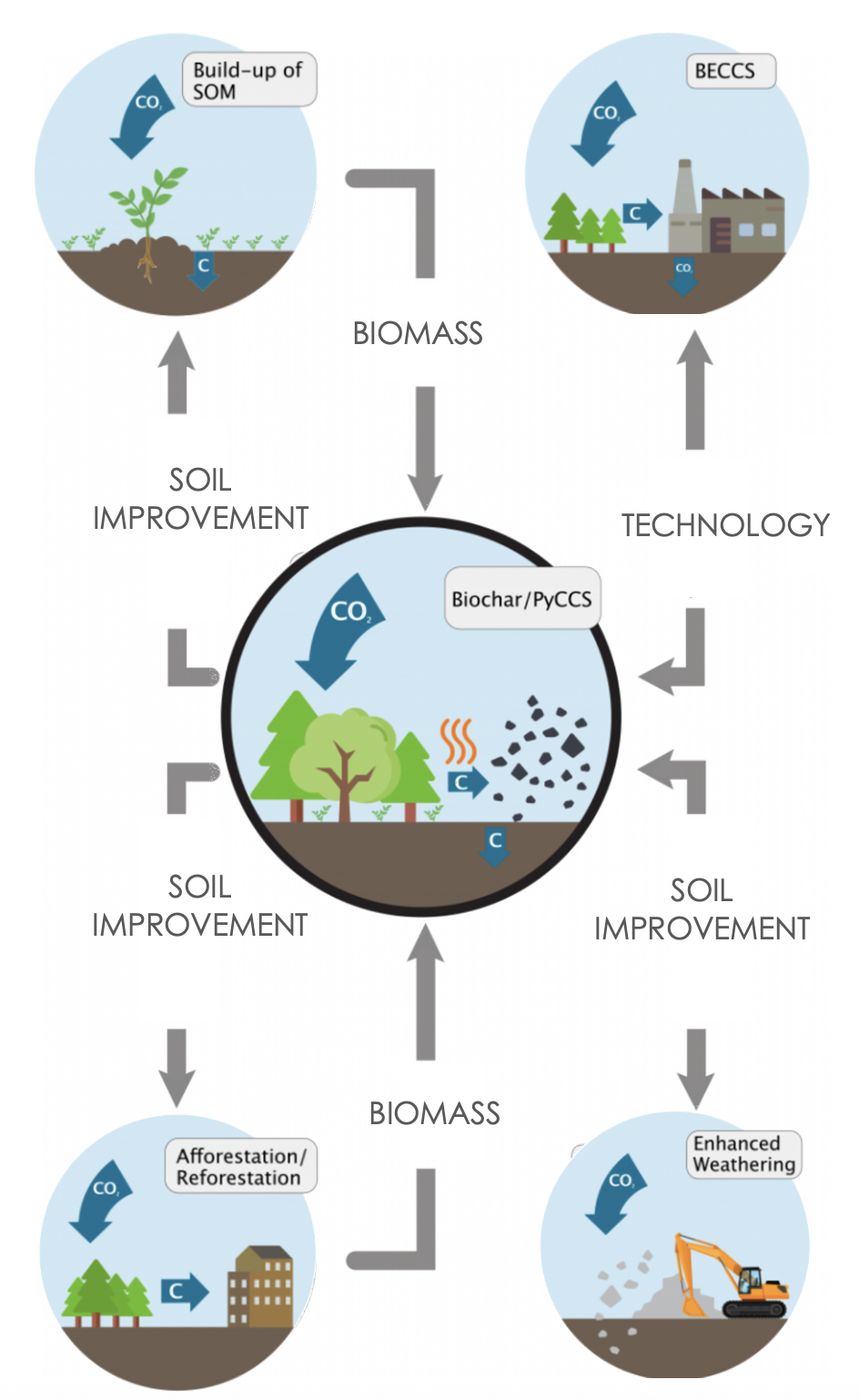
Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich material produced by heating organic biomass (such as crop residues, wood, or manure) in a low-oxygen environment (a process called pyrolysis).
In the context of regenerative agriculture, biochar serves multiple purposes: improving soil health, enhancing crop productivity, sequestering carbon, and promoting circular nutrient use.
In Southeast Asia, where agriculture is central to livelihoods and the environment faces challenges like soil degradation, nutrient loss, and greenhouse gas emissions, biochar offers a promising solution.
By combining biochar with crop nutrient management, farmers can improve soil fertility and water retention, reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers, and restore degraded lands.
Biochar aligns with the principles of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) by supporting Soil Health Improvement, Climate Change Mitigation, Circular Economy and Waste Management