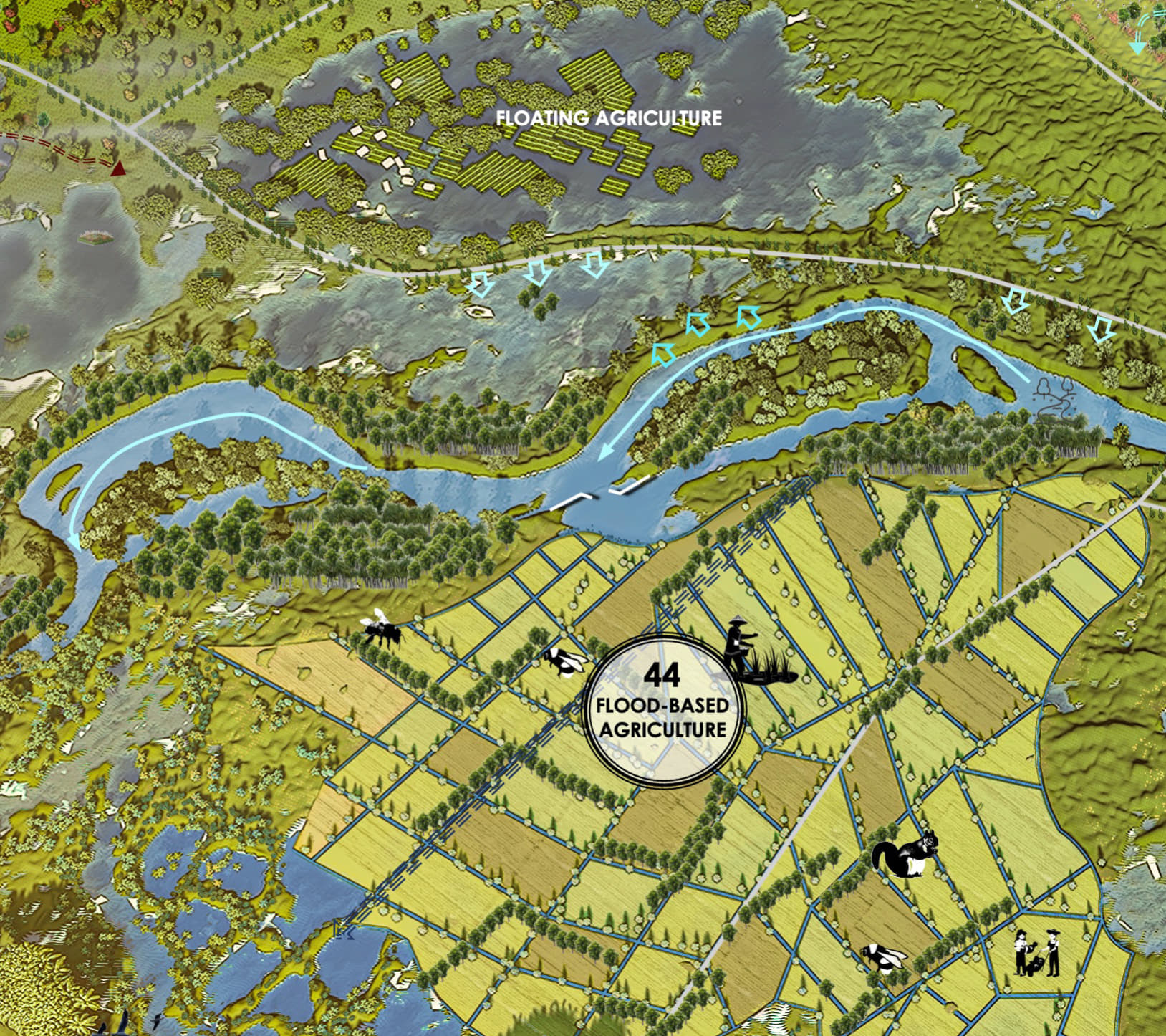
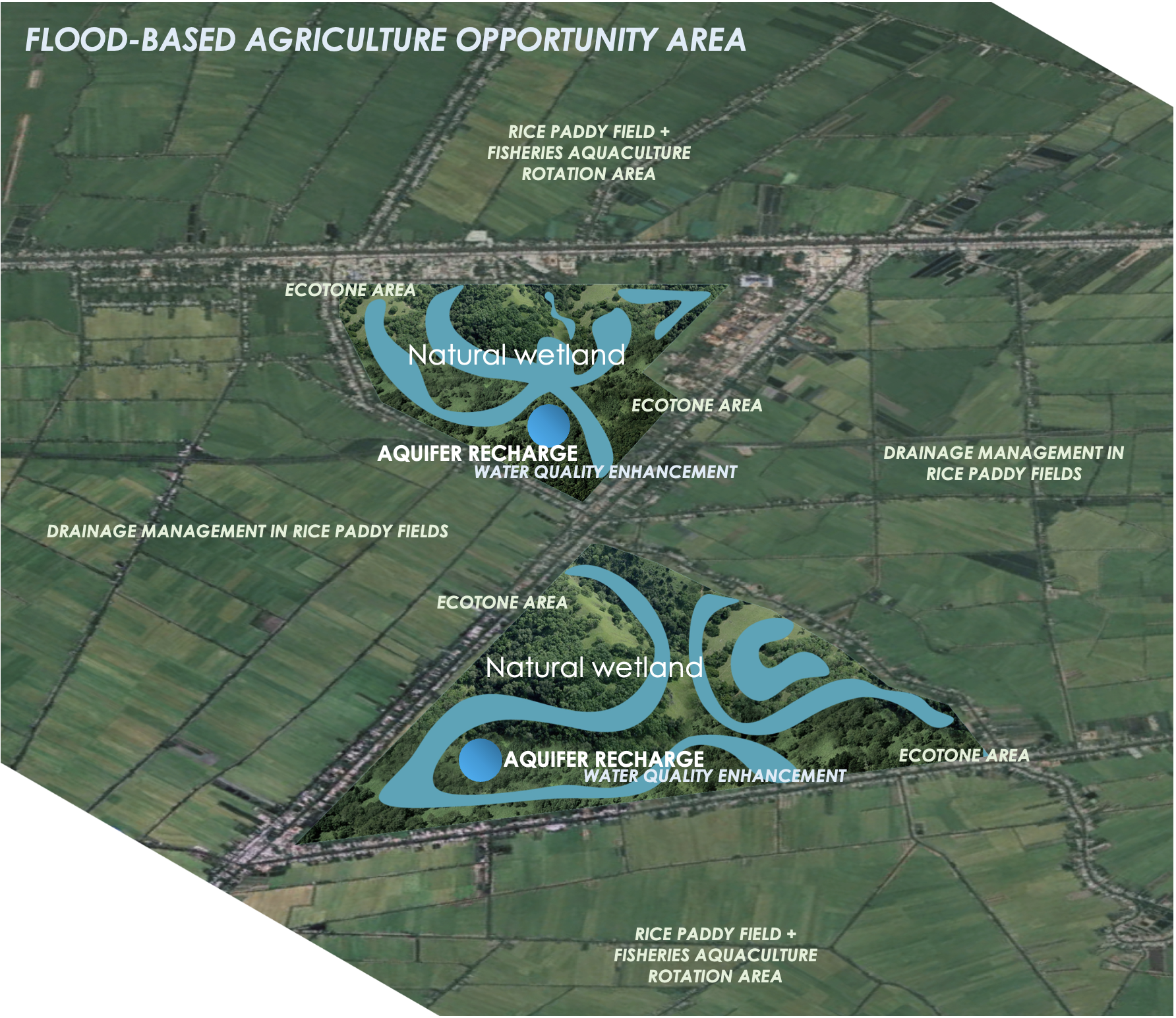
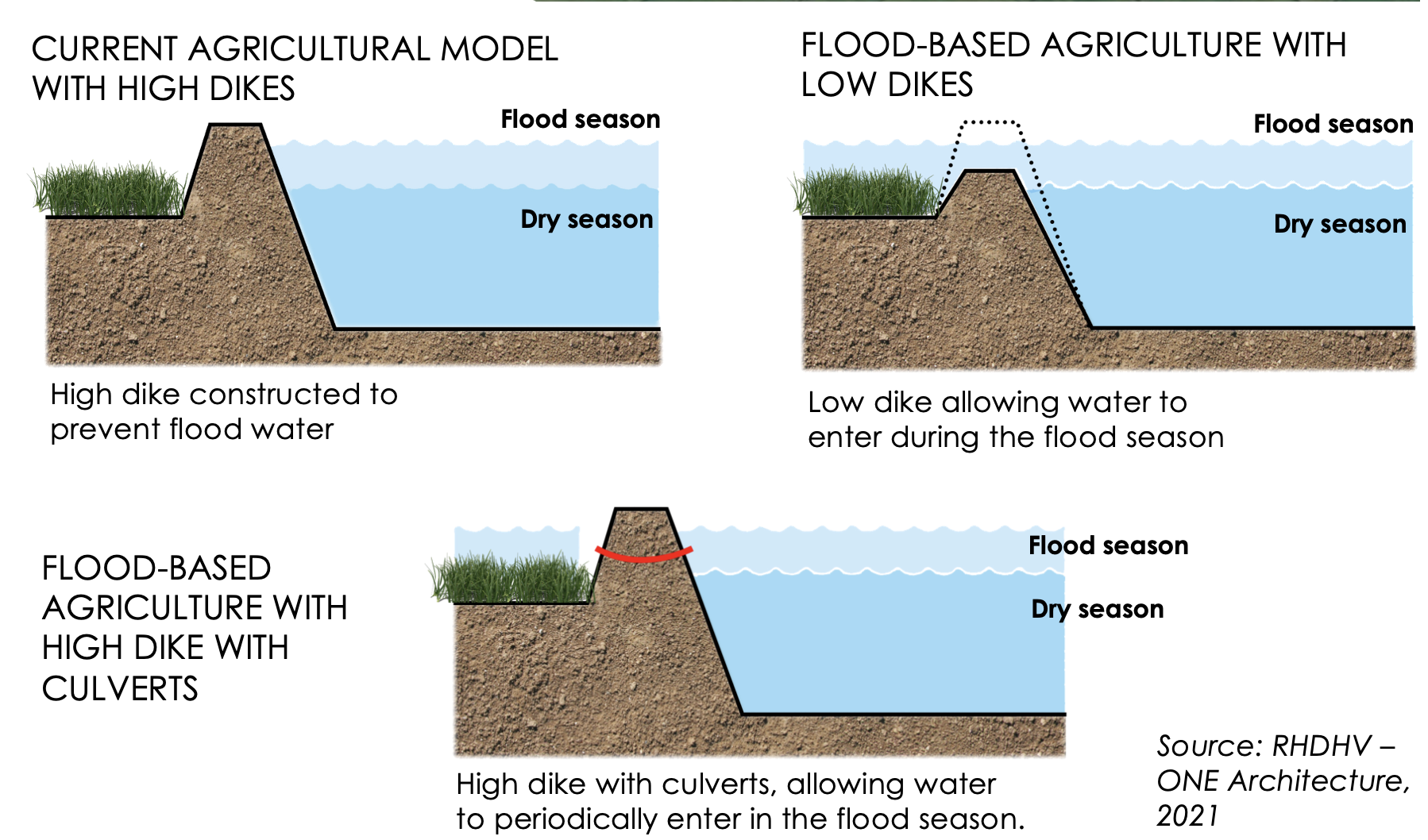
Flood-based agriculture is a nature-based solution (NbS) that leverages seasonal floods to enhance agricultural productivity, improve food security, and build climate resilience in flood-prone areas of Southeast Asia, such as the Mekong River Delta and Tonle Sap Biosphere.
This approach utilizes the natural inundation cycles to deposit nutrient-rich sediments, replenish soil fertility, and provide water for crops, reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and irrigation. Technically, it involves practices such as flood recession farming, floating crop cultivation, and integrated aquaculture-agriculture systems that maximize the benefits of water and sediment flows.
On a landscape level, it preserves floodplains, wetlands, and riparian ecosystems, which act as natural buffers against extreme weather events while enhancing biodiversity.
Socially, it supports rural livelihoods by offering sustainable income streams, promoting traditional knowledge, and strengthening community resilience to climate-induced disruptions such as droughts and floods.