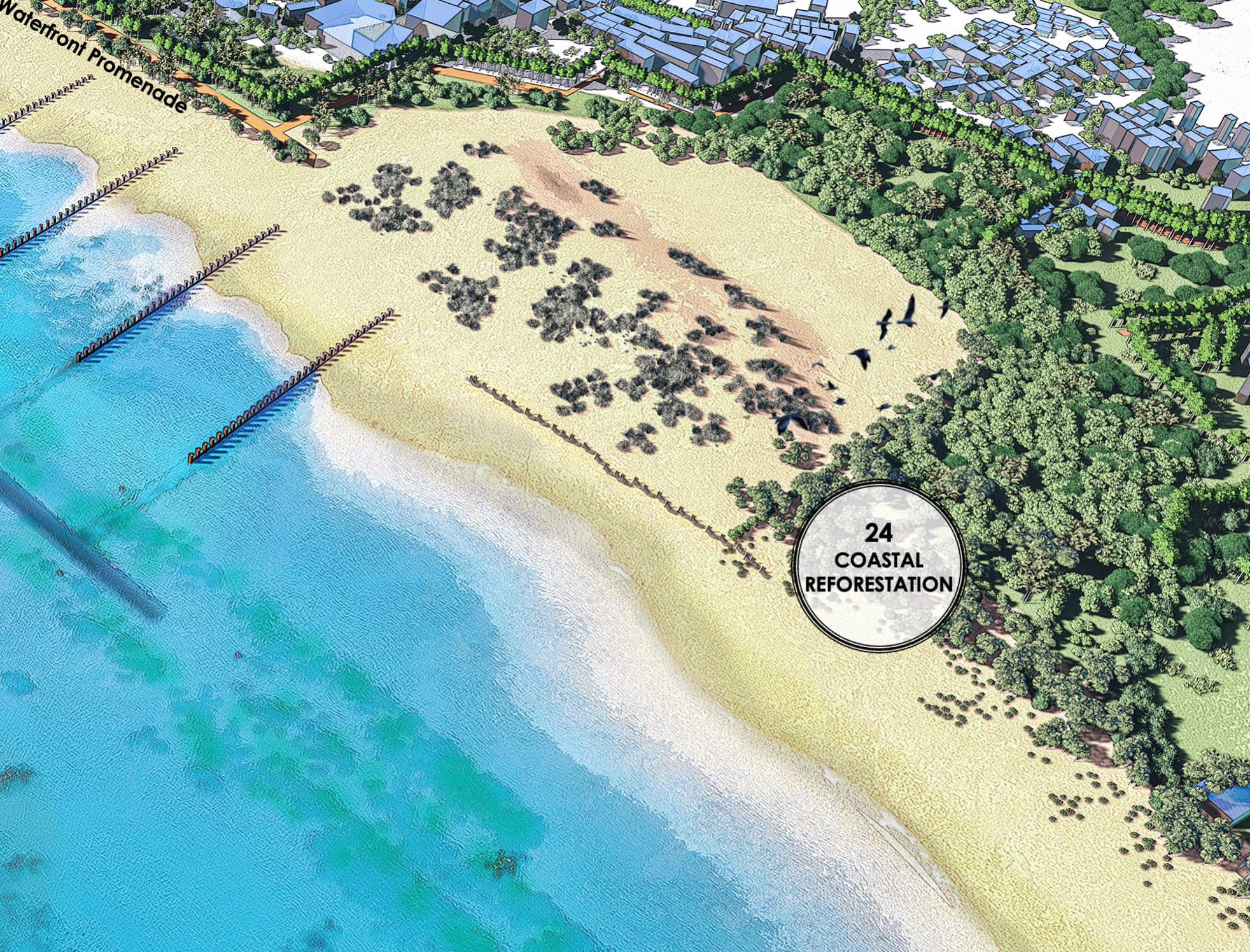
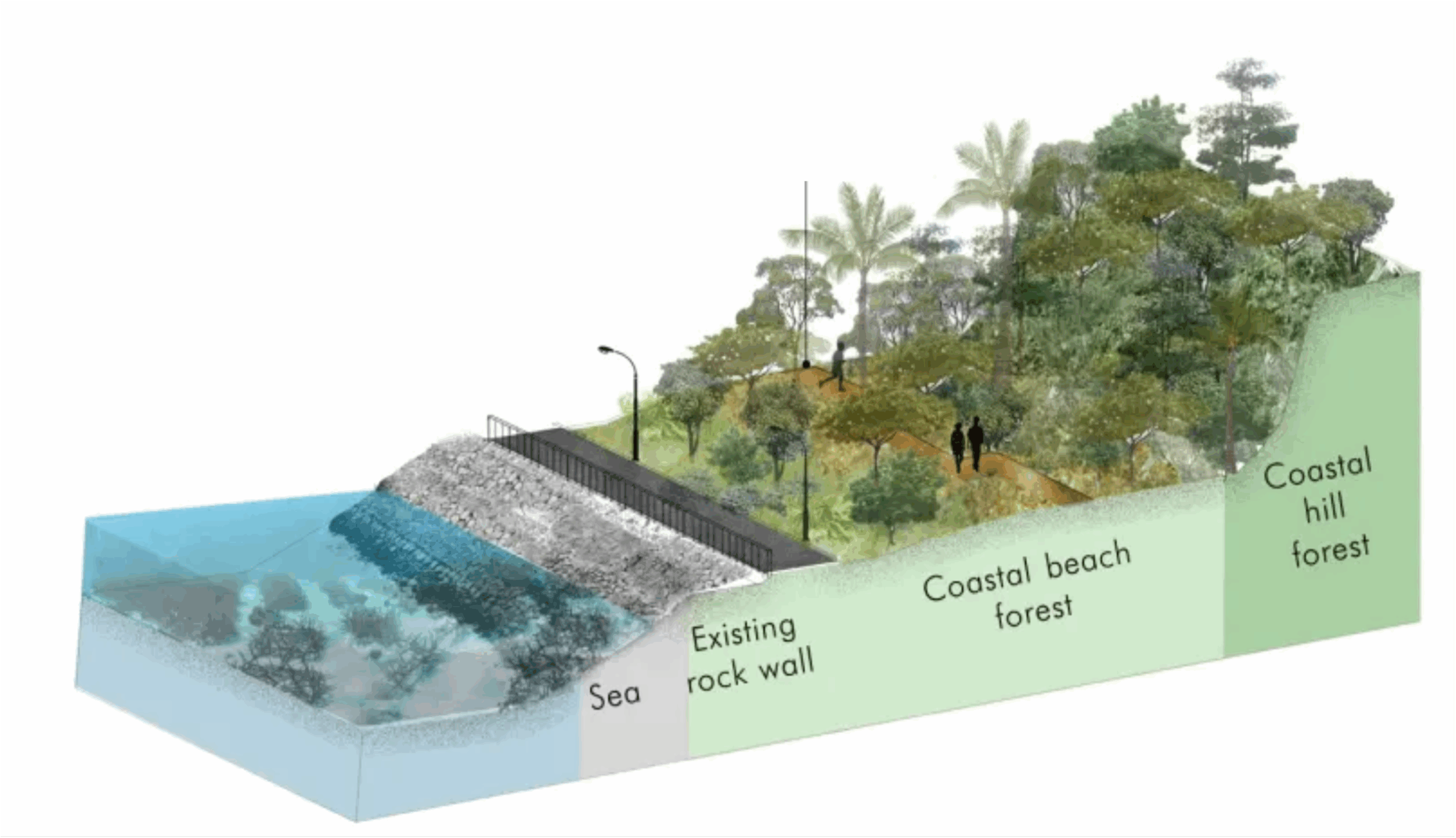
Coastal reforestation in wetland and sandy beach environments aims to restore natural vegetation adapted to saline, waterlogged, or nutrient-poor soils.
On sandy beaches, reforestation focuses on stabilizing dunes and loose sands using hardy species like sea oats, beach grass, and native shrubs. These plants anchor the soil, reduce erosion, and form windbreaks, creating a microhabitat that fosters further vegetation growth and protects inland areas from storm surges and salt spray.
In wetland coasts, mangroves, saltmarsh grasses, and other halophytic (salt-tolerant) species play a pivotal role. These plants trap sediment, reduce wave energy, and buffer coastlines from flooding. Their intricate root systems also provide essential habitat for aquatic life and improve water quality by filtering pollutants.