Riverbank stabilization prevents erosion and protects riverbanks from further degradation, while maintaining the natural integrity of the river system. This process is essential for preserving soil, reducing sedimentation in water, and preventing the loss of valuable land or infrastructure.
Stabilization techniques are employed to reinforce and protect riverbanks from the erosive forces of flowing water, especially during high-water events.
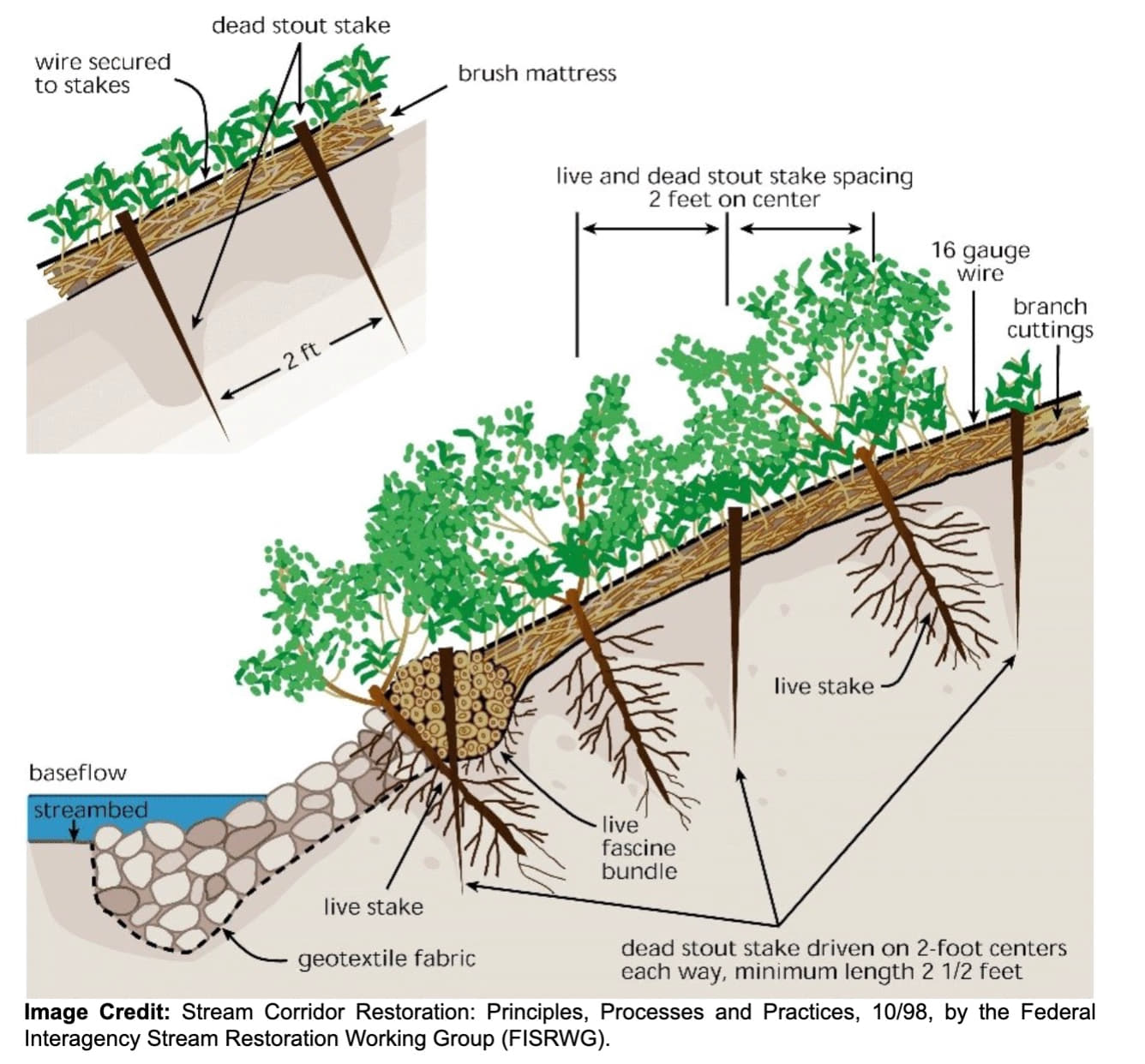
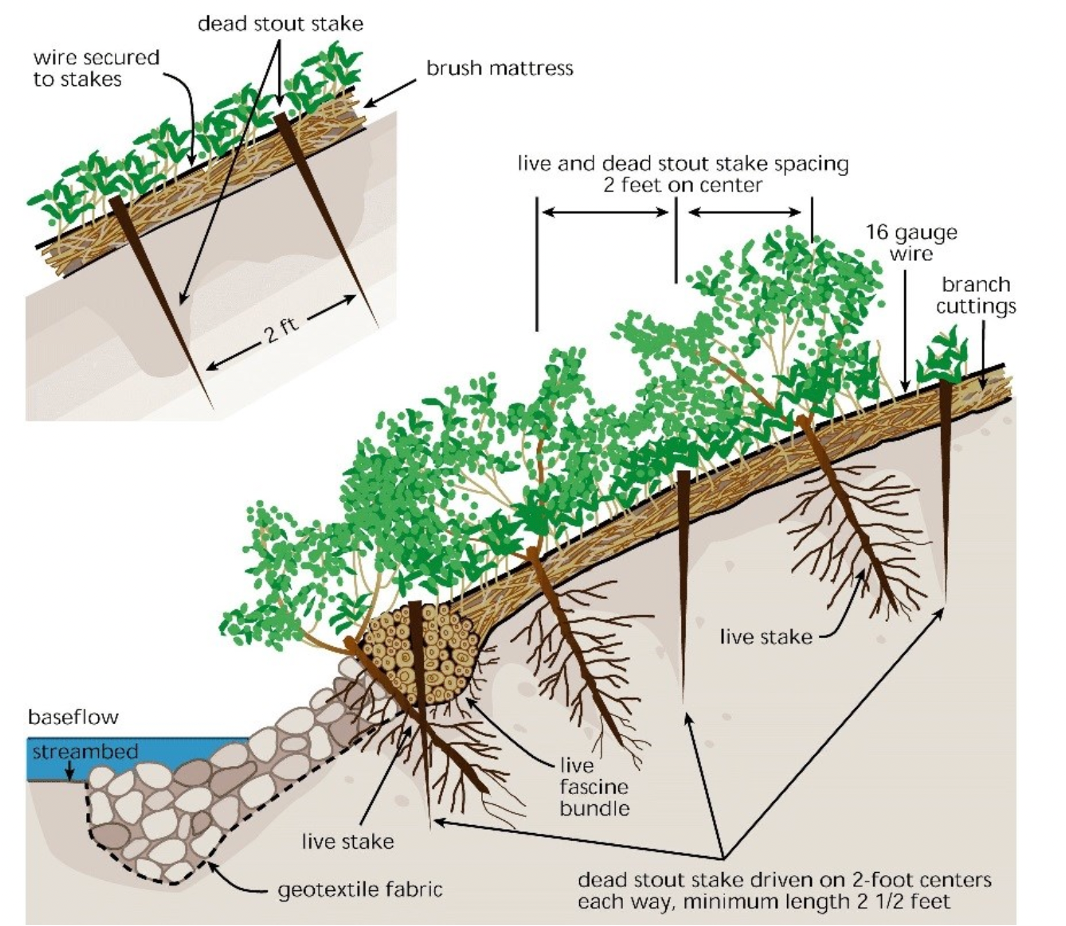
Efforts often involve a combination of structural and vegetative approaches. Structural methods can include the installation of large rocks or gravel, retaining walls, or engineered mats to physically support the riverbank.
Native, flood-tolerant plants such as grasses, shrubs, and trees are planted to anchor the soil with their root systems, reducing the impact of water flow and promoting soil cohesion. These plants also help filter excess nutrients, improve water quality, and provide habitat for various species.